6 Brain Architecture Mysteries That Neuroscience Can't Explain Yet
Discover 6 baffling brain architecture mysteries that challenge neuroscience. From chaotic synapses to glial cell secrets, explore why our minds remain unpredictable. Read more now.

6 Baffling Space Mysteries That Continue to Challenge Scientists and Defy Explanation
Explore 6 baffling space mysteries that challenge our understanding of the cosmos: Pioneer Anomaly, Wow! Signal, 'Oumuamua's strange acceleration, and more. Discover the unexplained.

The Fermi Paradox Explained: 5 Mind-Bending Theories About Why We Haven't Found Aliens Yet
Explore the Fermi Paradox: Why haven't we found aliens despite billions of stars? Discover Great Filter, Zoo Hypothesis, and other theories explaining cosmic silence.

6 Impossible Materials That Are Rewriting Physics Laws and Transforming Our Future
Discover 6 revolutionary materials redefining physics: metamaterials, self-healing concrete, programmable matter, topological insulators, frictionless surfaces & quantum spin liquids.

Plant Communication Secrets: The Hidden Networks and Chemical Messages Your Garden Is Hiding
Discover how plants communicate through electrical signals, chemical alerts, and fungal networks. Learn about plant memory, sound perception, and hidden forest conversations. Explore nature's secret language.

The Mathematical Constants That Secretly Control Every Living Thing and Cosmic Phenomenon
Discover how 7 mathematical constants secretly shape everything from flower spirals to galaxies. Explore nature's hidden code where golden ratio, pi, and Fibonacci numbers rule reality itself.
How Biological Clocks Control Every Living Thing on Earth (And Transform Your Daily Life)
Discover how biological clocks control sleep, health, and life cycles - from cellular timekeepers to magnetic navigation in animals. Learn the science behind your body's rhythms.

5 Mind-Bending Scientific Theories That Could Explain What Consciousness Really Is
Discover 5 groundbreaking scientific theories of consciousness - from quantum mechanics to predictive processing. Explore what makes you you in this ultimate mystery.

6 Revolutionary Deep Ocean Hydrothermal Vent Discoveries That Redefine Life on Earth
Discover 6 revolutionary deep ocean hydrothermal vent discoveries that transformed our understanding of extreme life. From chemosynthetic bacteria to giant tube worms thriving in toxic conditions, explore how these alien-like ecosystems challenge biology. Learn more about Earth's final frontier.

7 Mind-Bending Mathematical Paradoxes That Defy Logic and Challenge Reality
Explore 7 mind-bending mathematical paradoxes that challenge logical thinking. From Banach-Tarski to Gödel's Incompleteness Theorems, discover how these counterintuitive concepts reveal the limits of human understanding. Click to expand your mathematical horizons.

6 Mind-Bending Time Anomalies: How Physics Challenges Our Reality
Discover 6 mind-bending time anomalies physicists have measured that challenge our understanding of reality. From quantum retrocausality to black holes, explore how time may not be the straightforward concept we experience daily. Learn how physics reshapes our understanding of past and future.
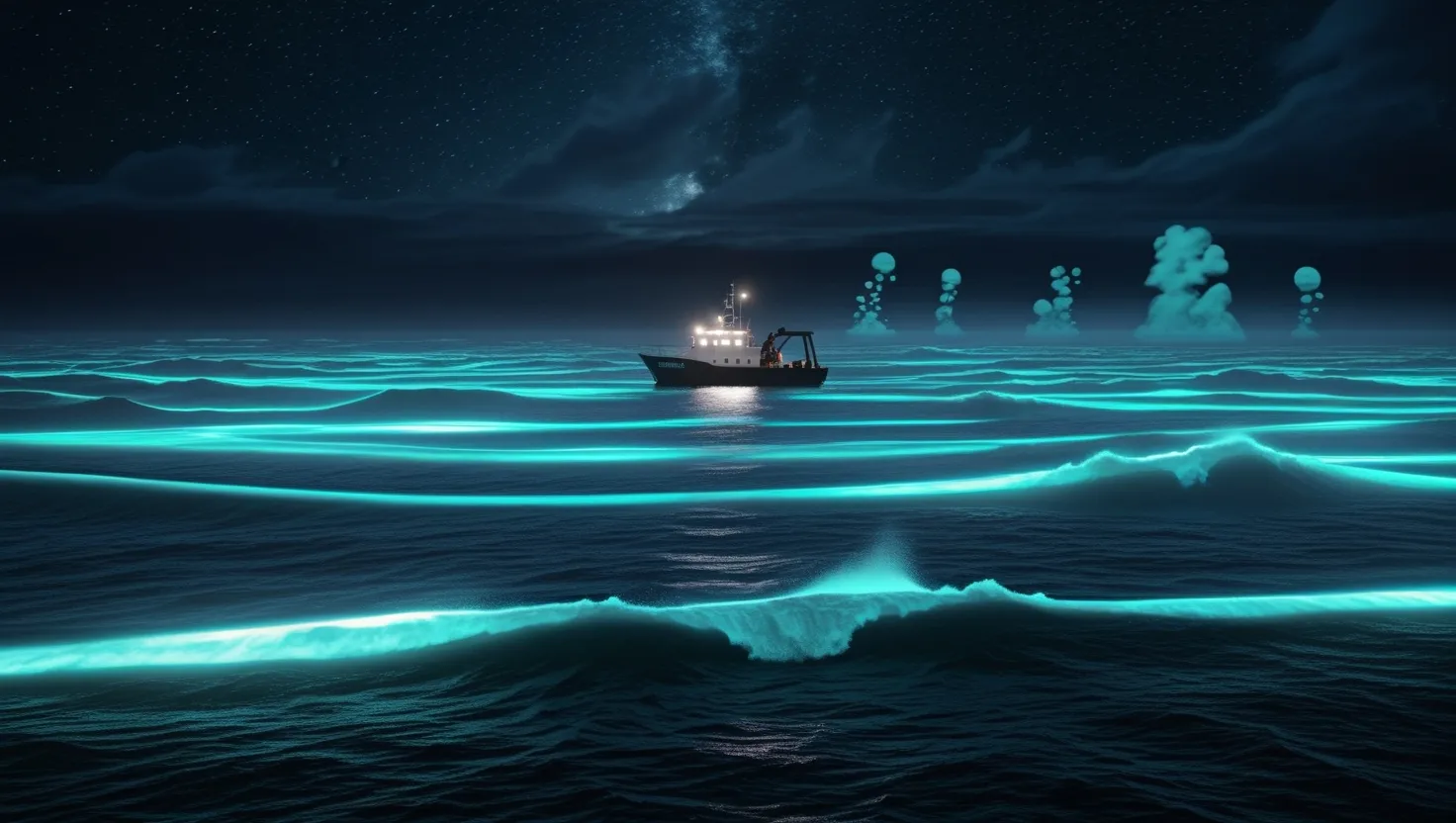

8 Ocean Mysteries That Challenge Modern Science: From Glowing Seas to Deep Storms
Discover 8 ocean mysteries that defy scientific explanation. From milky seas visible from space to bizarre deep currents, explore how these phenomena shape our planet and challenge our understanding. Learn what scientists are missing.
Revolutionary Medical Diagnostics: 7 Technologies Transforming Disease Detection and Patient Care
Discover revolutionary medical diagnostic technologies reshaping healthcare through AI, liquid biopsies, and portable tools. Learn how these innovations improve early detection and personalized treatment. Explore the future of medicine today.