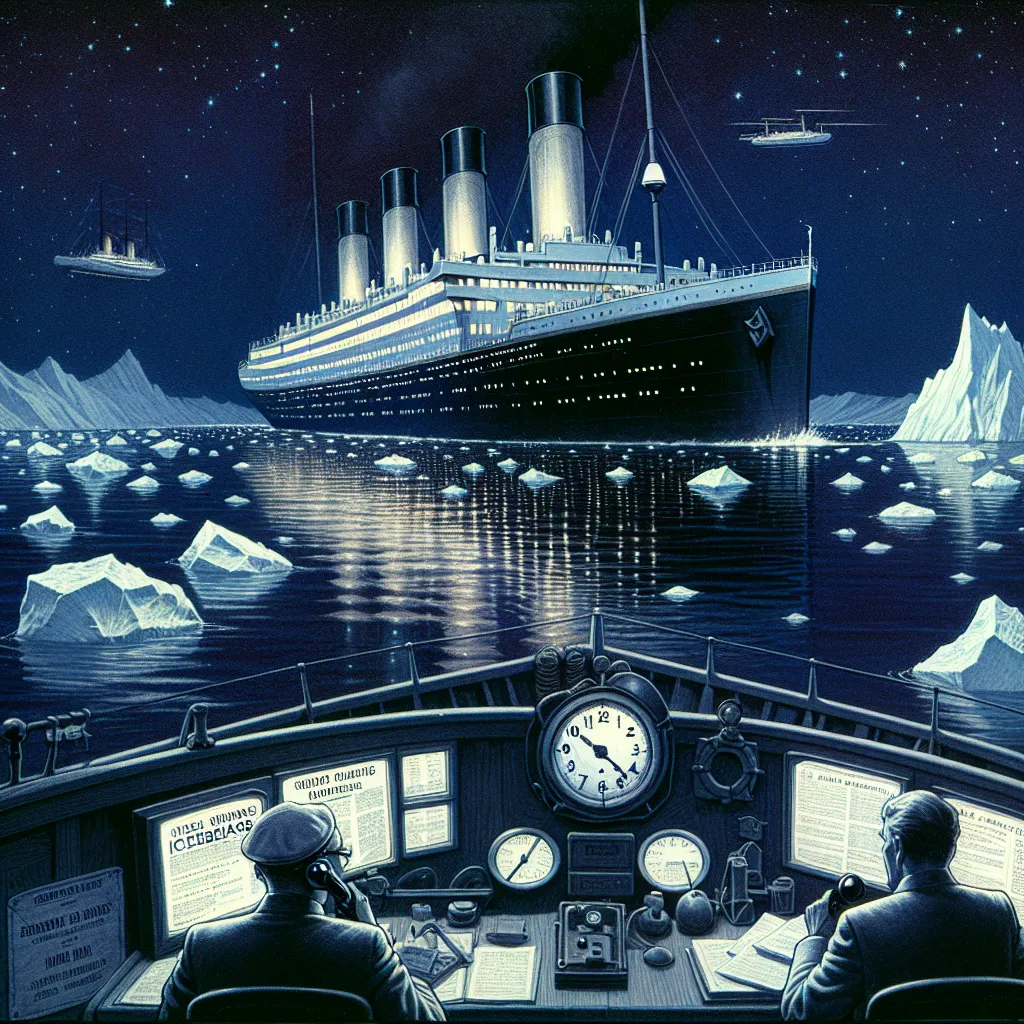
On the evening of April 14th, 1912, the Titanic altered its course, heading west across the Atlantic. Captain Smith believed they were in a safe zone of the Gulf Stream, where icebergs were apparently non-existent. However, that year, a significant phenomenon occurred, enabling icebergs to drift further south due to the Labrador Current, which formed a cold barrier around them. Depending on the Gulf Stream’s position, this cold water could travel deep into the North Atlantic shipping routes.
By 6 p.m., the steamship Californian spotted an iceberg, nearly 130 miles away from the Titanic, and sent a warning message. However, Phillips, one of Titanic’s wireless operators, was off duty while his assistant, Bride, ignored the message due to preoccupations with accounts. Despite their expertise, these wireless operators were underpaid and relied on sending passenger messages to make ends meet.
Hours later, the Californian’s warning remained unaddressed. That night, Captain Smith retired after doing a final check, discussing the calm sea with an officer. The flat calm suggested difficulty spotting icebergs since there would be no breaking water to give them away. Visibility relied solely on reflected light from icebergs.
The critical moment came at 9:45 p.m. Another ship, the SS Masaba, sent an urgent warning about icebergs just 50 miles from the Titanic. Phillips, interpreting it as non-urgent due to the lack of an MSG prefix, continued sending passenger messages, leaving the warning unseen. This, combined with a moonless, calm night, made spotting icebergs nearly impossible.
At full speed, Titanic was two hours away from the iceberg. The officers were mainly on the lookout for smaller, yet equally dangerous low-lying icebergs called growlers. These were harder to spot and posed a significant risk. Later that evening, fleet and lookout were scanning for growlers, unaware of the larger threat ahead—an iceberg as tall as the crow’s nest.
Shortly after, the watch changed. At 11 p.m., the iceberg was just 15 miles away. Despite discussions implying possible recklessness of maintaining high speed in such conditions, the norm across the Atlantic suggested otherwise. This tragic series of events, starting from misinterpreted messages to the difficulty in spotting icebergs on a calm, moonless night, led to the Titanic’s infamous encounter with the massive iceberg.