Hydraulic Fracturing: What You Need to Know
Since the industrial revolution, our energy consumption has skyrocketed. Most of this energy comes from fossil fuels like coal and natural gas. Lately, there’s been a lot of buzz around a controversial extraction method called hydraulic fracturing, or fracking.
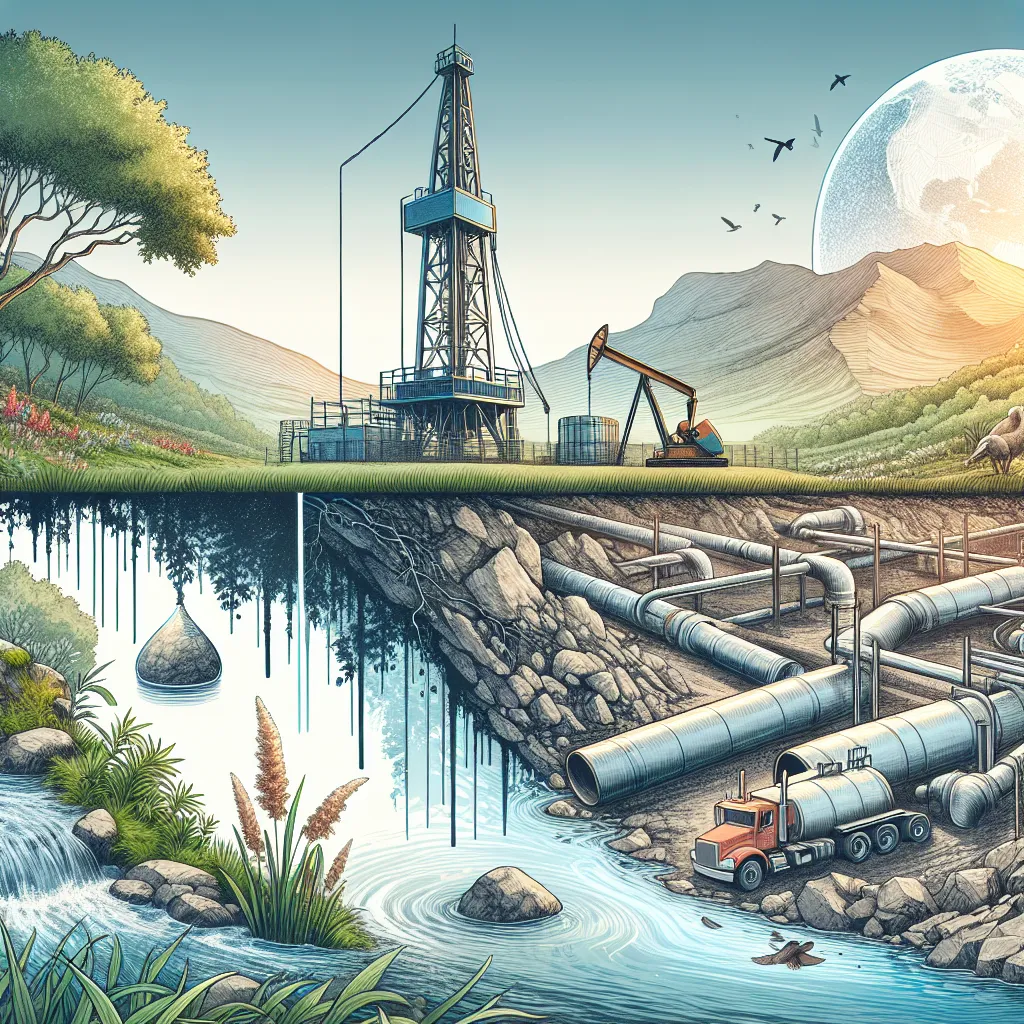
Fracking is a way to get natural gas from deep underground. It involves cracking open porous rock with a mix of water, sand, and chemicals to release the gas. While this technique has been around since the 1940s, it only boomed in the last decade, especially in the USA. This surge is because conventional gas sources are drying up, making more complex and costlier methods like fracking appealing and profitable.
Fracking works by drilling a vertical shaft several hundred meters deep, then drilling horizontally into the gas-rich rock layer. High-performance pumps then inject a fluid mixture that typically includes 8 million liters of water—equivalent to what 65,000 people use daily, several thousand tons of sand, and about 200,000 liters of chemicals. This mix creates tiny cracks in the rock, with sand keeping these cracks open and chemicals playing various roles, like killing bacteria and dissolving minerals. Most of the fluid is pumped back out, enabling the gas to flow and be collected. Once the gas is tapped out, the drill hole is sealed, often with the fracking fluid left underground.
However, fracking comes with significant risks. The primary concern is water contamination. Fracking uses a lot of fresh water, which becomes highly toxic afterward and can’t be cleaned sufficiently. Despite the known dangers, negligence has already led to contaminated water sources in the USA. What’s more alarming is the lack of long-term studies on how sealed fracking fluid behaves over time.
The chemicals in fracking fluid are another concern. These range from hazardous to extremely toxic and carcinogenic, like benzol or formic acid. Companies keep the exact chemical mix secret, but around 700 different agents can be used.
Fracking also impacts the environment by releasing greenhouse gases. The natural gas it recovers is mostly methane, which is 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas. Although burning natural gas is cleaner than coal, the overall climate impact of fracking is quite negative. The process itself demands a lot of energy, and the drill holes exhaust quickly, needing more frequent drilling than traditional wells. Plus, about 3% of the gas recovered escapes into the atmosphere during extraction.
Balancing the pros and cons, fracking offers a way to meet our demand for cheaper energy in the short to medium term. Yet, the long-term consequences, especially the risks to our drinking water, are still unknown and potentially severe.